Different groups use different words and phrases to describe the death of a baby during sleep. Refer to the following information to inform your discussions about safe infant sleep.
Sudden Unexpected Infant Death (SUID): An umbrella category that describes all sudden, unexpected infant deaths—those from known causes, such as an injury or accident, and those from unknown causes.
Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS): The sudden death of a baby younger than 1 year of age that doesn’t have a known cause, even after a full investigation. Healthcare providers, law enforcement, and others investigate infant deaths to figure out what caused them. This investigation includes a complete autopsy, examining the death scene, and reviewing the clinical history. If they cannot determine a cause of death for the baby or explain why the baby died, the medical examiner or coroner may categorize the death as SIDS.
Other sleep-related infant deaths: 1 Infant deaths linked to how or where a baby sleeps or slept. They can include deaths from the following:
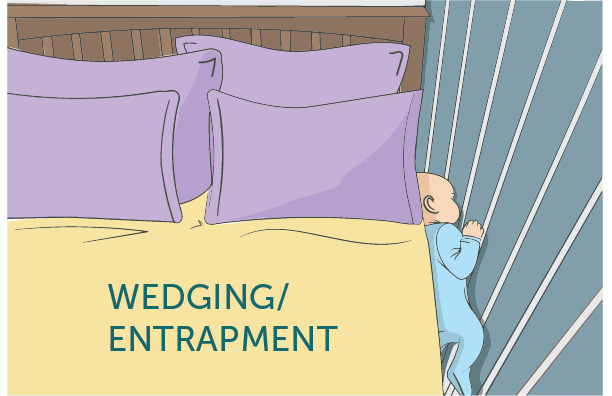
- Entrapment or wedging: Baby’s body or head gets stuck between two objects, such as a mattress and wall, bed frame, or furniture.
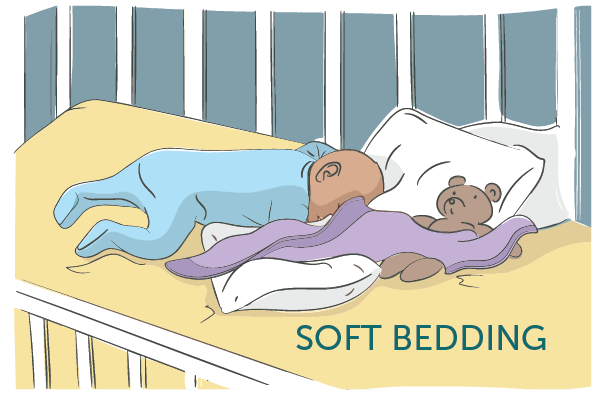
- Suffocation: Something, such as a pillow or an adult’s arm, covers baby’s face and nose.
- Strangulation: Something presses on or wraps around baby’s neck or head.
These deaths are different from Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS), but they are a type of Sudden Unexpected Infant Death (SUID).
Room sharing: Keeping baby in the same room as parents but on a separate sleep surface made for infants. Keeping a safety-approved crib,* bassinet, or portable play yard right next to the adult bed makes it easier to feed, comfort, and check on the baby during the night without having to get completely out of bed. The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends room sharing for at least the baby’s first 6 months to reduce the risk of SIDS and other sleep-related deaths.
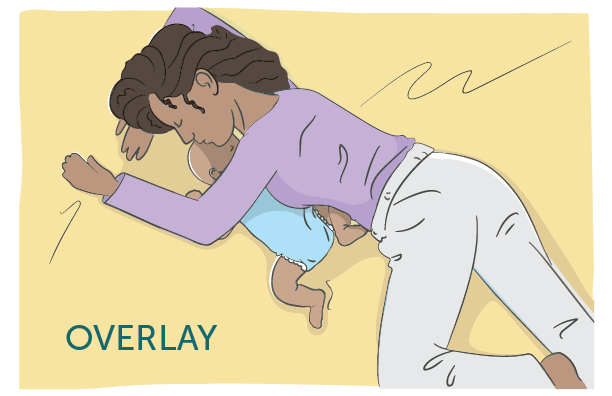
Bed sharing: Sharing a sleep surface—such as an adult bed, couch, or armchair—with a baby. Bed sharing greatly increases the risk of SIDS and other sleep-related infant deaths, such as accidental suffocation or entrapment. Learn more about the risks of bed sharing.
Co-sleeping: A general term for sleeping near or with an infant. This term can describe both room sharing and bed sharing. Therefore, AAP and other provider groups recommend against using this term.
Crib or cot death: An older term for SIDS that focused on the sleep area. Because SIDS can occur in any sleep area, such as a crib, bassinet, or portable crib/play yard, the term is no longer used.

